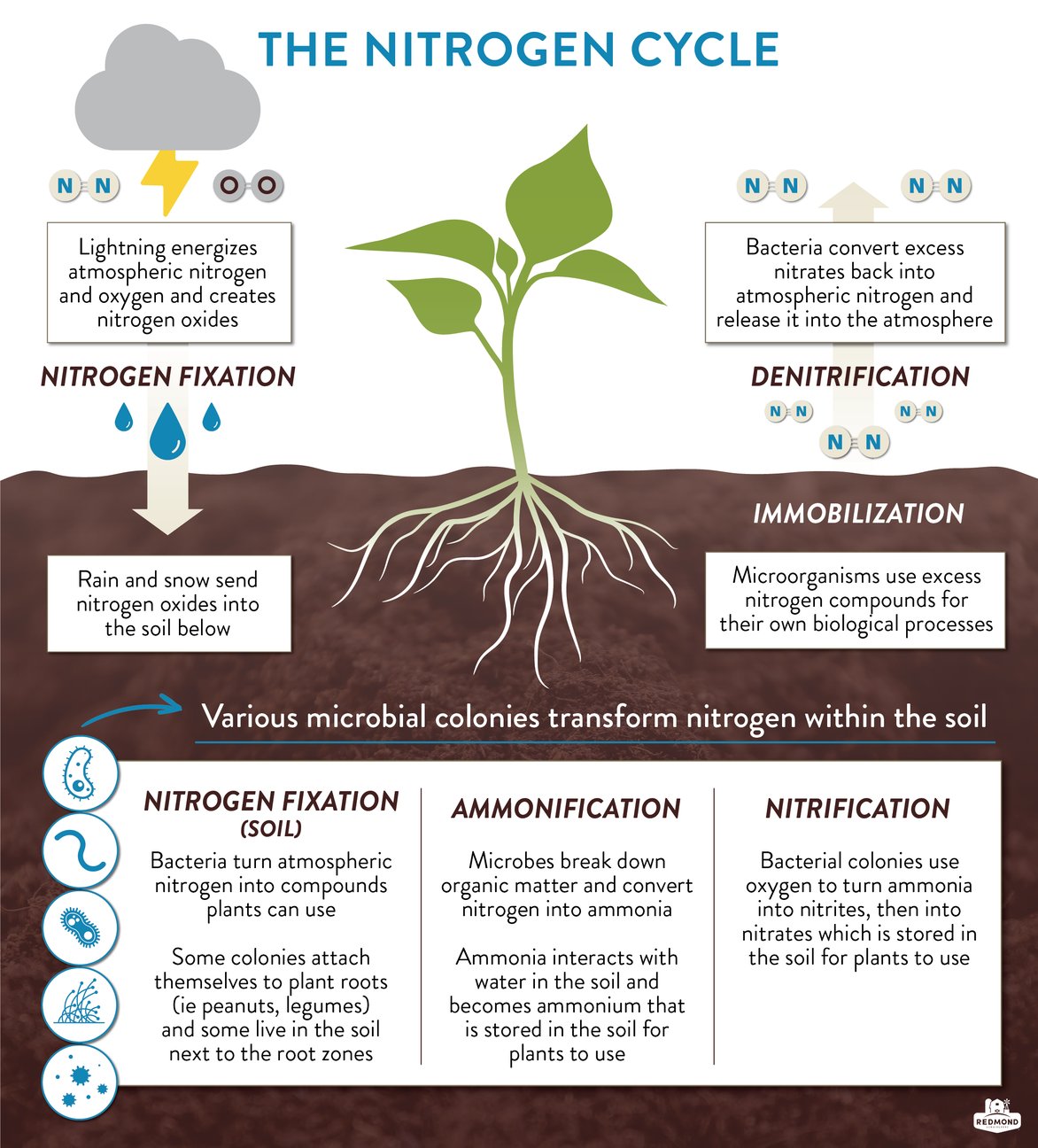
Plants Take Nitrogen In The Form Of
Plants Take Nitrogen In The Form Of - Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions, and. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. In the nitrogen cycle (ecology), it is usually described that plants can use nitrogen. Nitrifying bacteria in the soil. This inorganic form of nitrogen. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium.
Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions, and. In the nitrogen cycle (ecology), it is usually described that plants can use nitrogen. Nitrifying bacteria in the soil. This inorganic form of nitrogen. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground.
Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. This inorganic form of nitrogen. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions, and. Nitrifying bacteria in the soil. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium. In the nitrogen cycle (ecology), it is usually described that plants can use nitrogen.
The Nitrogen Cycle determines the amount of nitrogen available for
Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions, and. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because. Nitrifying bacteria in.
How Plants Obtain Nitrogen for Growth? ABTL Enzymes
Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. This inorganic form of nitrogen. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. Nitrifying bacteria in the soil. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,.
How do plants fix nitrogen? John Innes Centre
Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. This inorganic form of nitrogen. Nitrifying bacteria in the soil. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots.
NitrogenFixing Edible Plants Learn articles Orchard of Flavours
Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions,.
Balkan Ecology Project Nitrogen Fixing Plants
In the nitrogen cycle (ecology), it is usually described that plants can use nitrogen. This inorganic form of nitrogen. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions, and. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3).
Nitrogen cycle
Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. In the nitrogen cycle (ecology), it is usually described that plants can use nitrogen. Nitrifying bacteria in the soil. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions, and.
Nitrogen Fixation
Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions, and. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form.
How Do Plants Use Nitrogen?
Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. This inorganic form of nitrogen. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions,.
Where Do Plants Get Nitrogen Plants BG
Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium. In the nitrogen cycle (ecology), it is usually described that plants can use nitrogen. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because. Plants get nitrogen in the form.
Plants And The Nitrogen Cycle
Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because. This inorganic form of nitrogen. Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,.
In The Nitrogen Cycle (Ecology), It Is Usually Described That Plants Can Use Nitrogen.
Plants take up nitrogen compounds through their roots. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate,. Plants get nitrogen in the form of nitrates (n o 3) from the ground. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil as both nh₄⁺ and no₃⁻ ions, but because.
This Inorganic Form Of Nitrogen.
Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate and ammonium. Plants uptake and assimilate nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate, ammonium ions, and. Nitrifying bacteria in the soil.