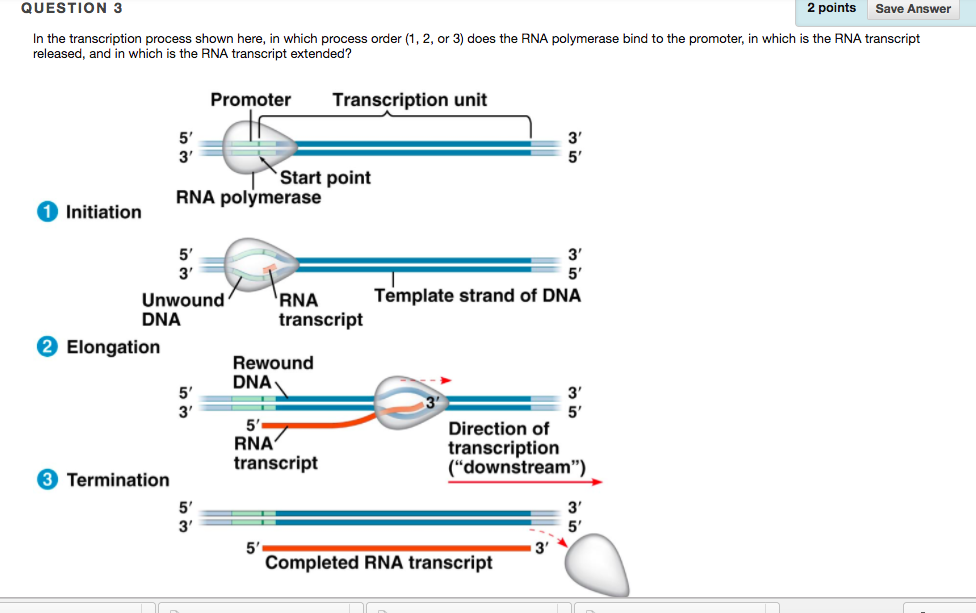
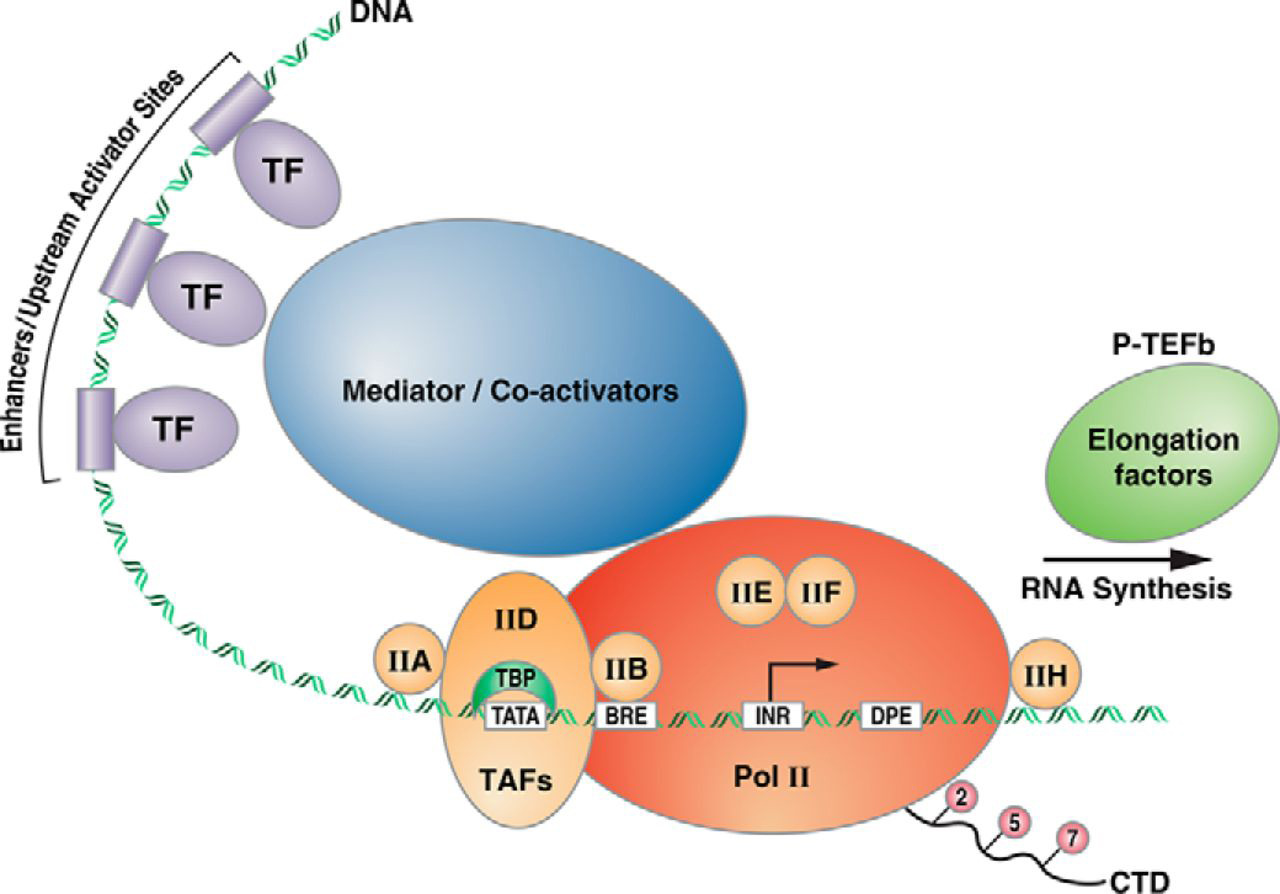
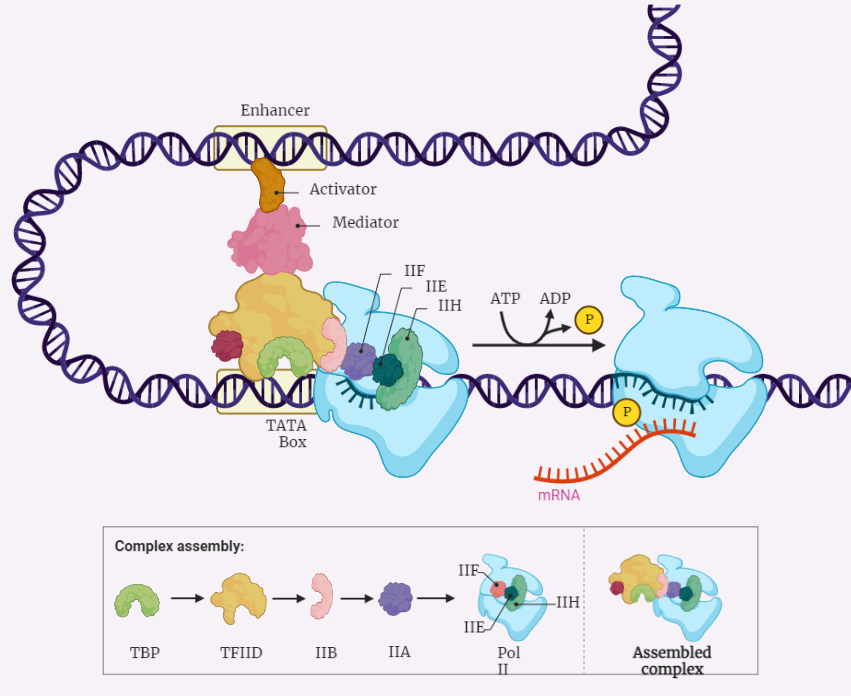
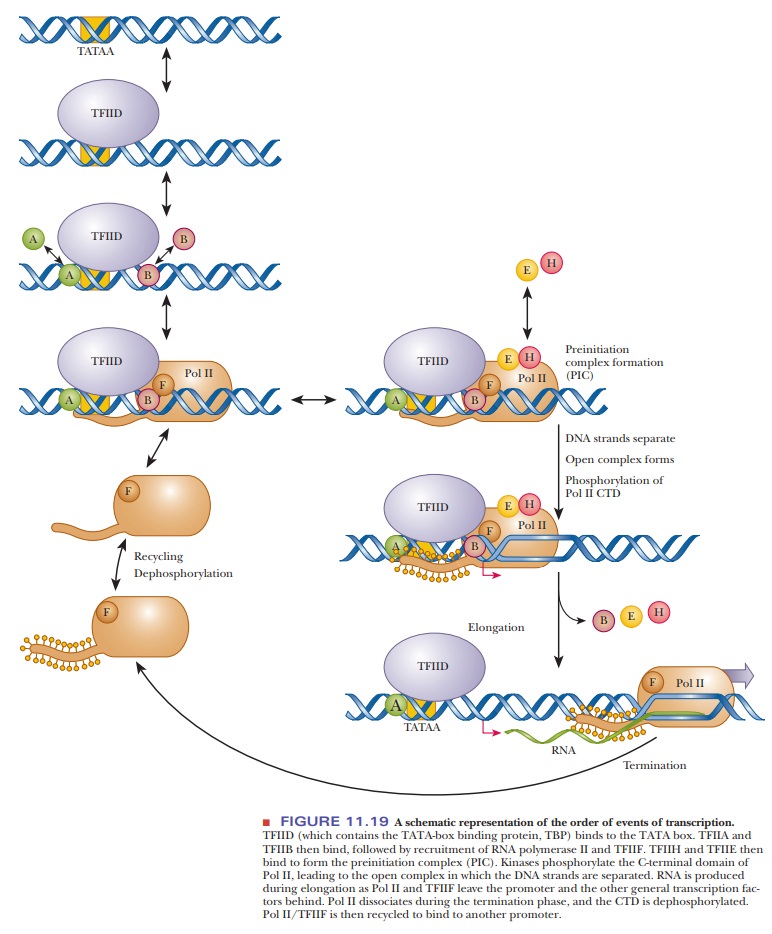
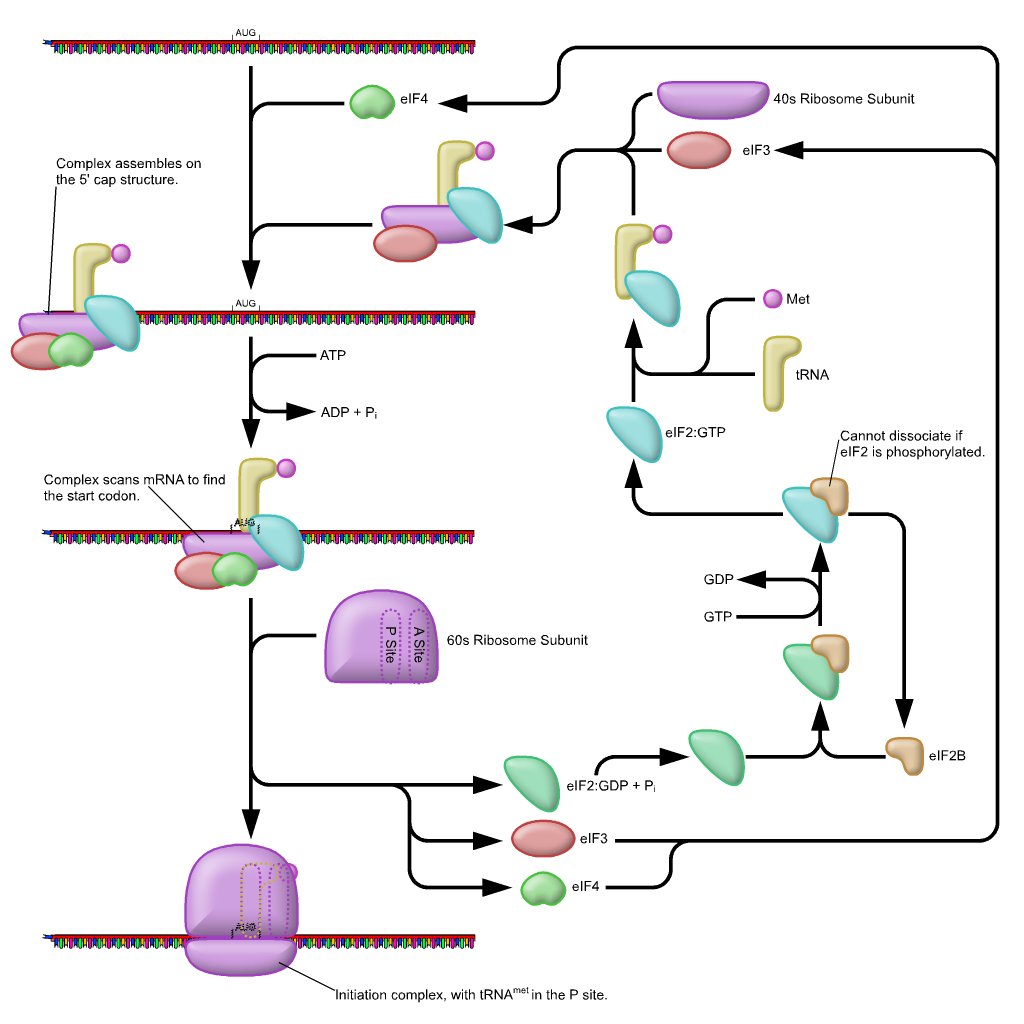How Do Eukaryotic Transcription Factors Help Form The Initiation Complex
How Do Eukaryotic Transcription Factors Help Form The Initiation Complex - The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. The complete assembly of transcription. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna.
The complete assembly of transcription. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors.
Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. The complete assembly of transcription. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors.
Solved QUESTION 4 Which of the following components does NOT
Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. The complete assembly of transcription. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors.
Transcription Initiation Complex Eukaryote
The complete assembly of transcription. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna.
Transcription Initiation Complex Eukaryote
Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. The complete assembly of transcription. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex.
Eukaryotic transcription Rethink Biology Notes
Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed.
Transcription Initiation Complex Eukaryote
The complete assembly of transcription. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors.
Figure 1 from Eukaryotic transcription initiation Semantic Scholar
The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require.
Transcription Initiation Complex Eukaryote
The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. The complete assembly of transcription. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex.
Transcription Initiation Complex Eukaryote
Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. The complete assembly of transcription.
Transcription Initiation Complex Eukaryote
Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. The complete assembly of transcription. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex.
Eukaryotic Transcription Boundless Biology
Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and. Thus, transcription in the eukaryotic system appeared to require distinct initiation factors. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. The complete assembly of transcription. Eukaryotic initiation factors eif1, eif3, eif4, and eif5 help bring the 43s complex.
Thus, Transcription In The Eukaryotic System Appeared To Require Distinct Initiation Factors.
The complete assembly of transcription. The simple answer to this question is that eukaryotes have developed a more complex. Initiation of transcription, which results in the complex of proteins, including the rna. Transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and.