Devil S Staircase Math
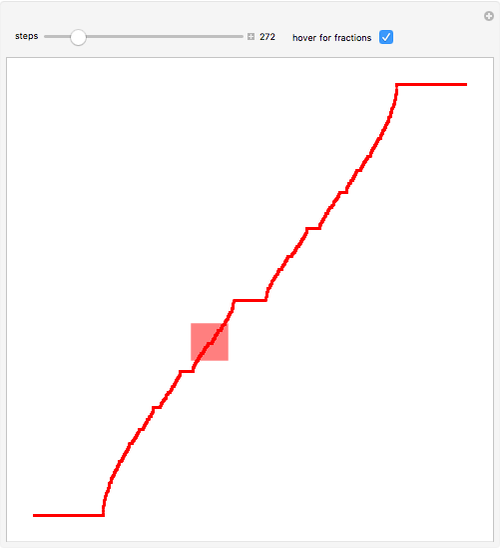
Devil S Staircase Math - The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. Call the nth staircase function. The graph of the devil’s staircase. [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the.
The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. The graph of the devil’s staircase. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. Call the nth staircase function. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}.
Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. The graph of the devil’s staircase. Call the nth staircase function. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. Consider the closed interval [0,1].
Devil's Staircase by dashedandshattered on DeviantArt
The graph of the devil’s staircase. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}.
Devil's Staircase Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Call the nth staircase function. The graph of the devil’s staircase. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone.
Devil’s Staircase Math Fun Facts
The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; The graph of the devil’s staircase..
Devil's Staircase Continuous Function Derivative
The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. Call the nth staircase function. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup.
Devil's Staircase by RawPoetry on DeviantArt
Consider the closed interval [0,1]. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; Call the nth staircase.
Devil's Staircase by PeterI on DeviantArt
Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: Call the nth staircase function..
Staircase Math
The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. The graph of the devil’s staircase. Call the nth staircase function. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone.
The Devil's Staircase science and math behind the music
Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest.
Devil's Staircase by NewRandombell on DeviantArt
The graph of the devil’s staircase. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The result is a monotonic.
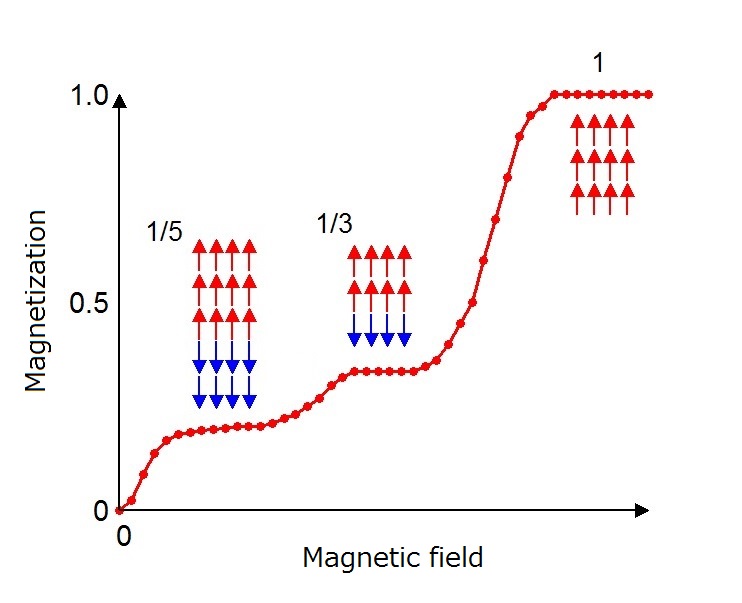
Emergence of "Devil's staircase" Innovations Report
• if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; Call the nth staircase function. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The graph of the devil’s staircase.
[X] 3 = 0.X 1X 2.X N−11X N+1., Replace The.
Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone.
The First Stage Of The Construction Is To Subdivide [0,1] Into Thirds And Remove The Interior Of The Middle Third;
Call the nth staircase function. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. The graph of the devil’s staircase. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: